Description of DES:-
DES is the archetypal block cipher—an algorithm that takes a fixed-length string of plaintext bits and transforms it through a series of complicated operations into another ciphertext bitstring of the same length. In the case of DES, the block size is 64 bits. DES also uses a key to customize the transformation, so that decryption can supposedly only be performed by those who know the particular key used to encrypt. The key ostensibly consists of 64 bits; however, only 56 of these are actually used by the algorithm. Eight bits are used solely for checking parity, and are thereafter discarded. Hence the effective key length is 56 bits.
The key is nominally stored or transmitted as 8 bytes, each with odd parity. According to ANSI X3.92-1981 (Now, known as ANSI INCITS 92-1981) One bit in each 8-bit byte of the KEY may be utilized for error detection in key generation, distribution, and storage. Bits 8, 16,..., 64 are for use in ensuring that each byte is of odd parity.
Like other block ciphers, DES by itself is not a secure means of encryption, but must instead be used in a mode of operation. FIPS-81 specifies several modes for use with DES. Further comments on the usage of DES are contained in FIPS-74. Decryption uses the same structure as encryption, but with the keys used in reverse order. (This has the advantage that the same hardware or software can be used in both directions.)
Working:-
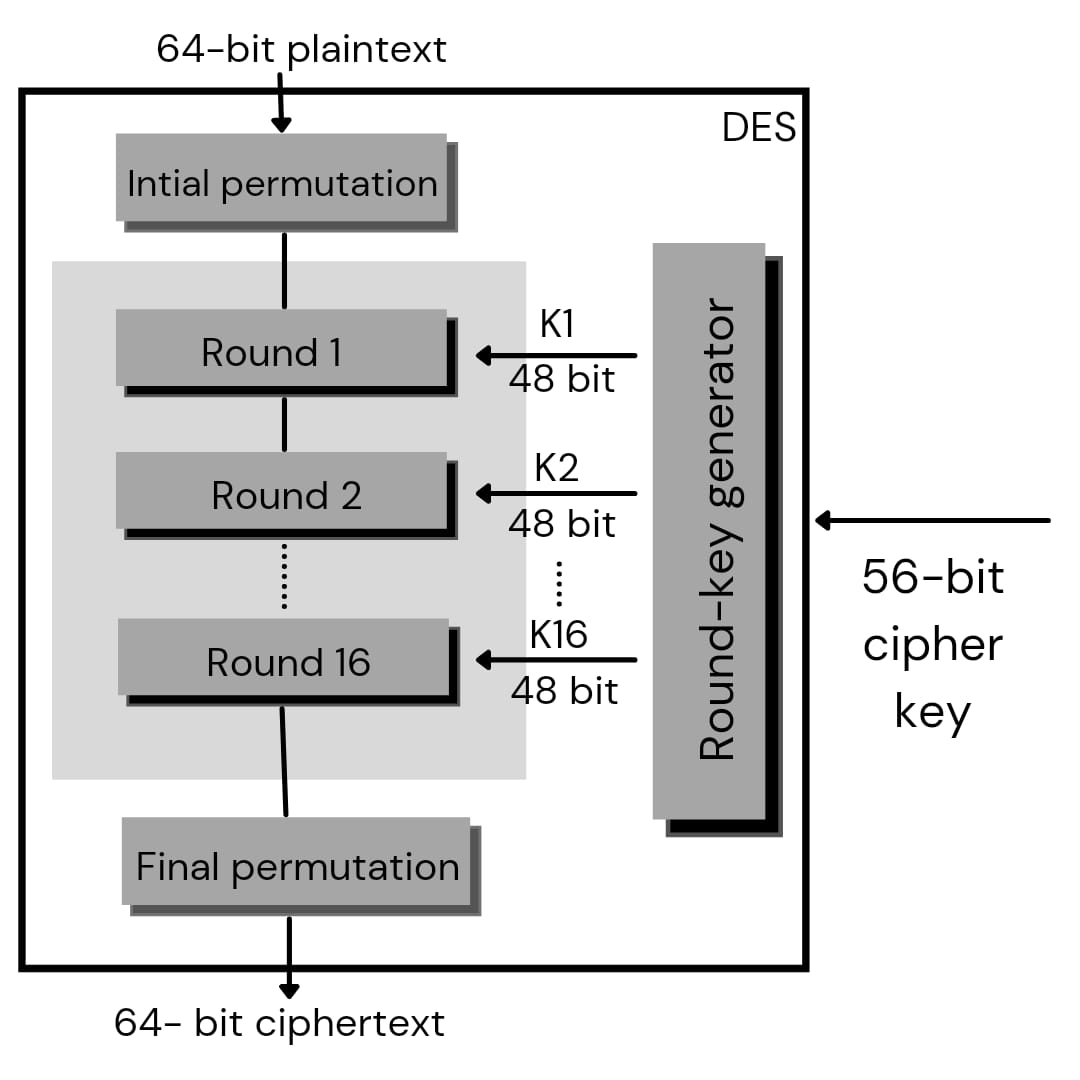
- The algorithm's overall structure has 16 identical stages of processing, termed rounds. There is also an initial and final permutation, termed IP and FP, which are inverses (IP "undoes" the action of FP, and vice versa). IP and FP have no cryptographic significance, but were included in order to facilitate loading blocks in and out of mid-1970s 8-bit based hardware.
- Before the main rounds, the block is divided into two 32-bit halves and processed alternately; this criss-crossing is known as the Feistel scheme. The Feistel structure ensures that decryption and encryption are very similar processes—the only difference is that the subkeys are applied in the reverse order when decrypting. The rest of the algorithm is identical. This greatly simplifies implementation, particularly in hardware, as there is no need for separate encryption and decryption algorithms.
- The ⊕ symbol denotes the exclusive-OR (XOR) operation. The F-function scrambles half a block together with some of the key. The output from the F-function is then combined with the other half of the block, and the halves are swapped before the next round. After the final round, the halves are swapped; this is a feature of the Feistel structure which makes encryption and decryption similar processes.
- The Feistel (F) function Edit The F-function, depicted in Figure 2, operates on half a block (32 bits) at a time and consists of four stages:
- Expansion: the 32-bit half-block is expanded to 48 bits using the expansion permutation, denoted E in the diagram, by duplicating half of the bits. The output consists of eight 6-bit (8 × 6 = 48 bits) pieces, each containing a copy of 4 corresponding input bits, plus a copy of the immediately adjacent bit from each of the input pieces to either side.
- Key mixing: the result is combined with a subkey using an XOR operation. Sixteen 48-bit subkeys—one for each round—are derived from the main key using the key schedule .
- Substitution: after mixing in the subkey, the block is divided into eight 6-bit pieces before processing by the S-boxes, or substitution boxes. Each of the eight S-boxes replaces its six input bits with four output bits according to a non-linear transformation, provided in the form of a lookup table. The S-boxes provide the core of the security of DES—without them, the cipher would be linear, and trivially breakable.
- Permutation: finally, the 32 outputs from the S-boxes are rearranged according to a fixed permutation, the P-box. This is designed so that, after permutation, the bits from the output of each S-box in this round are spread across four different S
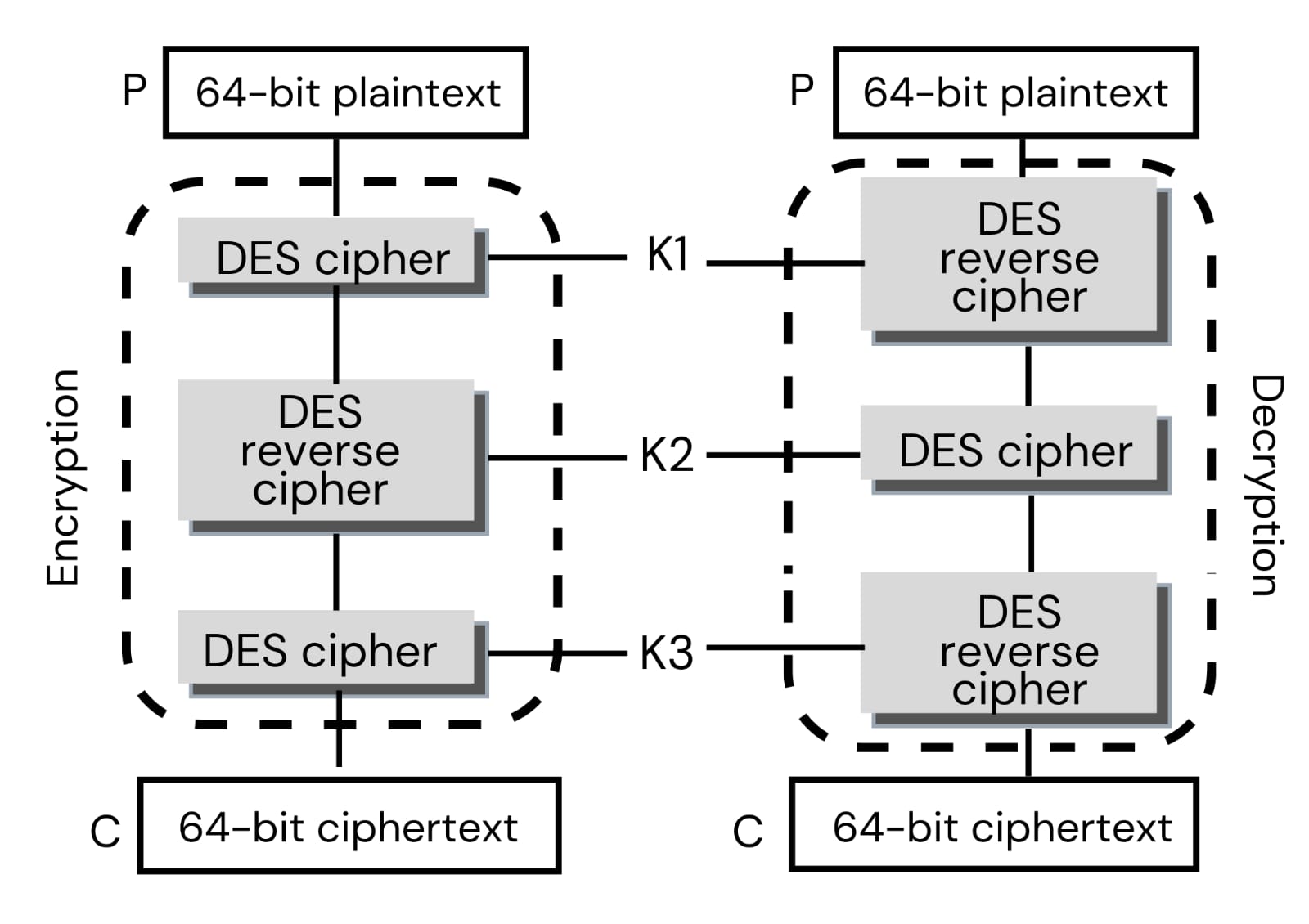
Algorithm of DES:-
Beginning square is a plain book block which contains 64 pieces of plain content which is given to introductory change where the reworking of 64-digit plain content happens which is then given to cycle 1 to 16 then it is given to conclusive stage which produces encoded information. In this 64-bit symmetric key is utilized out of which 56-bit key is utilized in the calculation, the eighth bit of each 8-byte is eliminated at first.
This eighth piece is an odd equality bit. This 56-cycle information is given through PC1 where reworking of 56-bit happens. Then, at that point the left shift moves the piece. For cycle 1,2,9,16 there is just 1-digit shift in the key, for different rounds 2-bit shift in key. This is then given to PC2 where an arbitrary 48 piece key is chosen. In cycle 1 the 64 bit information is splitted into 2*32 piece . One of 32 bit information goes through extension where 32 bit information is extended to 48 piece. This is then Xor with a 48bit key. Then, at that point this is again packed to 32 pieces. This 32 cycle is then joined with staying 32bit plain content and in this manner 64bit code text is produced.
Consider from here, Information encryption standard (DES) has been found defenseless against extremely amazing assaults and hence, the ubiquity of DES has been discovered somewhat on decay. DES is a square code, and scrambles information in squares of size of 64 digit each, which means 64 pieces of plain content goes as the contribution to DES, which produces 64 pieces of code text. A similar calculation and key are utilized for encryption and unscrambling, with minor contrasts.
The key length is 56 pieces We have referenced that DES utilizes a 56 cycle key. In reality, the underlying key comprises of 64 pieces. Be that as it may, before the DES interaction even beginnings, each eighth piece of the key is disposed of to create a 56 cycle key. That is bit position 8, 16, 24, 32, 40, 48, 56 and 64 are disposed of. Subsequently, the disposing of each eighth piece of the key delivers a 56-digit key from the first 64-bit key. DES depends on the two central ascribes of cryptography: replacement (additionally called as disarray) and rendering (likewise called as dissemination). DES comprises of 16 stages, every one of which is known as a round. Each round plays out the means of replacement and rendering. Allow us currently to talk about the expansive level strides in DES.
In the initial step, the 64 cycle plain content square is given over to an underlying Permutation (IP) work. The underlying change performed on plain content. Next the underlying change (IP) produces two parts of the permuted block; says Left Plain Text (LPT) and Right Plain Text (RPT). Presently each LPT and RPT go through 16 rounds of encryption. Eventually, LPT and RPT are rejoined and a Final Permutation (FP) is performed on the consolidated square The consequence of this interaction produces 64 digit figure text. Introductory Permutation (IP) –
As we have noticed, the Initial change (IP) happens just a single time and it occurs before the first round. It recommends how the rendering in IP ought to continue, as displayed in figure. For instance, it says that the IP replaces the main piece of the first plain content square with the 58th piece of the first plain content, the second piece with the 50th piece of the first plain content square, etc. This is only jugglery of touch places of the first plain content square. A similar guideline goes after the wide range of various piece jobs which show in the figure. As we have noted get-togethers done, the subsequent 64-bit permuted text block is partitioned into two half squares. Every half square comprises of 32 pieces, and every one of the 16 rounds, thus, comprises of the wide level advances illustrated in figure.
Steps:-
Step1 Key Change:-
We have noticed that the underlying 64-cycle key is changed into a 56-digit key by disposing of each eighth piece of the underlying key. Consequently, for each a 56-bit key is accessible. From this 56-bit key, an alternate 48-bit Sub Key is produced during each round utilizing an interaction called key change. For this the 56 digit key is separated into equal parts, every one of 28 pieces.
These parts are circularly moved left by a couple of positions, contingent upon the round. For instance, if the round number 1, 2, 9 or 16 the shift is finished by just situation for different rounds, the roundabout shift is finished by two positions. The quantity of key pieces moved per round is displayed in figure. After a fitting movement, 48 of the 56 pieces are chosen.
For choosing 48 of the 56 pieces the table shows in the figure given beneath. For example, after the shift, bit number 14 maneuvers on the principal position, bit number 17 actions on the subsequent position, etc. On the off chance that we notice the table cautiously, we will understand that it contains just 48 piece positions.
Spot number 18 is disposed of (we won't discover it in the table), like 7 others, to lessen a 56-cycle key to a 48-piece key. Since the key change measure includes stage just as determination of a 48-piece sub-set of the first 56-bit key it is called Compression Permutation. In light of this pressure change strategy, an alternate subset of key pieces is utilized in each round. That makes DES difficult to break.
Step2 Expansion Permutation:-
Review that get-togethers change, we had two 32-bit plain content regions called Left Plain Text(LPT) and Right Plain Text(RPT). During the extension change, the RPT is extended from 32 pieces to 48 pieces. Pieces are permuted also thus called as extension change. This occurs as the 32 digit RPT is separated into 8 squares, with each square comprising of 4 pieces. Then, at that point, every 4 bit square of the past advance is then extended to a relating 6 cycle block, i.e., per 4 digit block, 2 additional pieces are added.
This cycle brings about development just as stage of the information bit while making yield. Key change measure packs the 56-bit key to 48 pieces. Then, at that point the development change measure extends the 32-cycle RPT to 48-bits. Presently the 48-piece key is XOR with 48-piece RPT and coming about yield is given to the subsequent stage, which is the S-Box replacement.
Discription of TDES:-
Triple Data Encryption Standard (DES) is a sort of automated cryptography where square code calculations are applied multiple times to every information block. The key size is expanded in Triple DES to guarantee extra security through encryption abilities. Each square contains 64 pieces of information. Three keys are alluded to as pack keys with 56 pieces for each key. There are three entering choices in information encryption norms:
All keys being free, Key 1 and key 2 being free keys, Every one of the three keys being indistinguishable, Key choice #3 is known as triple DES. The triple DES key length contains 168 pieces yet the key security tumbles to 112 pieces, Techopedia Explains Triple DES
Triple DES is profitable in light of the fact that it has an altogether estimated key length, which is longer than most key lengths partnered with other encryption modes. Notwithstanding, the DES calculation was supplanted by the Advanced Encryption Standard by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST). Hence, the Triple DES is currently viewed as out of date. However, it is normal utilized related to Triple DES. It gets from single DES however the method is utilized in three-fold and includes three sub keys and key cushioning when fundamental, for example, cases where the keys should be expanded to 64 pieces long. Known for its similarity and adaptability, programming can without much of a stretch be changed over for Triple DES consideration. In this manner, it may not be close to as old as considered by NIST.
Triple DES encodes input information multiple times. The three keys are alluded to as k1, k2 and k3. This innovation is contained inside the norm of ANSIX9.52. Triple DES is in reverse viable with customary DES.
Attack:-
New impact assaults against triple-DES, Blowfish break HTTPS meetings, Inheritance codes, for example, triple-DES and Blowfish are defenseless against Sweet32 assaults, which let aggressors decode HTTPS meetings even without the encryption key, CSO Online logo, NEWS, New impact assaults against triple-DES, Blowfish break HTTPS meetings, Heritage codes, for example, triple-DES and Blowfish are defenseless against Sweet32 assaults, which let aggressors decode HTTPS meetings even without the encryption key, digital assault stock picture, By Fahmida Y. Rashid, Supporter, InfoWorld, AUG 25, 2016 5:17 AM PT
There is presently a reasonable, generally quick assault on 64-bit block figures that allows assailants to recuperate confirmation treats and different accreditations from HTTPS-secured meetings, a couple of French specialists said. Heritage figures Triple-DES and Blowfish need to go the method of the wrecked RC4 figure: Deprecated and crippled all over the place.
Named Sweet32, specialists had the option to take confirmation treats from HTTPS-ensured traffic utilizing triple-DES (3DES) and Blowfish and recuperate login certifications to have the option to get to casualty accounts, said the analysts, Karthikeyan Bhargavan and Gaëtan Leurent of INRIA in France. The assault features why it is fundamental for destinations to quit utilizing inheritance codes and move up to present day, safer codes.
"We show that an organization aggressor who can screen an extensive Triple-DES HTTPS association between an internet browser and a site can recuperate secure HTTP treats by catching around 785 GB of traffic. In our confirmation of-idea demo, this assault at present takes under two days, utilizing vindictive Javascript to create traffic," said Bhargavan and Leurent. They are relied upon to introduce the full paper in October at the 23rd ACM Conference on Computer and Communications Security.
Sweet32 is a crash assault against triple-DES (3DES) and Blowfish in figure block tying (CBC) mode. In CBC mode, input crashes lead to XOR of two message blocks. At the point when loads of message blocks are scrambled with a similar key in this mode, crashes become more probable, which prompts getting the substance of two distinctive message blocks as yield. Assailants can focus on a casualty's validation treat by tricking them to a malignant site and infusing JavaScript into the casualty's program. JavaScript over and again sends HTTP questions to a site the casualty is signed into, and each solicitation will incorporate the validation treat.
The specialists found that if the assailants send no less than 232 inquiries and catch every one of the solicitations, they can ultimately see an impact and recuperate the substance of the treat. Additionally ON CSO: The 15 most exceedingly terrible information security breaks of the 21st century "A significant prerequisite for the assault is to send countless solicitations in similar TLS association. Accordingly, we need to discover customer and workers that arrange the utilization of Triple-DES, yet additionally trade an enormous number of HTTP demand in similar TLS association (without rekeying). This is conceivable utilizing a persevering HTTP association, as characterized in HTTP/1.1 (Keep-Alive). On the customer side, all programs that we tried (Firefox, Chrome, Opera) will reuse a TLS association as long as the worker keeps it open," the scientists said.
Blowfish and 3DES are as yet upheld in TLS, IPsec, SSH, and different conventions and notable locales, for example, Nasdaq.com Walmart.com actually support these heritage figures. Most of OpenVPN associations and between 1% and 2 percent of the Internet's traffic might be helpless to Sweet32, the analysts assessed. The execution utilized in OpenSSL is additionally influenced, albeit the OpenSSL maintainers asserted the assault didn't uncover a basic shortcoming. OpenVPN 2.3.12 accompanies an admonition about Blowfish shortcomings and secure setup guidance for managing Sweet32. OpenSSL 1.0.2 and 1.0.1 will move 3DES from the "HIGH" watchword to "MEDIUM" catchphrase and backing it naturally, the more up to date OpenSSL 1.1.0 will presently don't accumulate the code as a feature of the default assemble. Directors needing to utilize the heritage figure in OpenSSL 1.1.0 should utilize the 'empower frail ssl-codes' design alternative, and surprisingly then, at that point, the code is permitted distinctly in the 'MEDIUM' catchphrase. Significant programs producers are making changes which would focus on safer codes over 3DES.
The procedures and standards used to create the assault are surely known in cryptographic circles. The specialists decreased the intricacy and time expected to execute the assault. "While the standards behind this assault are notable, there's consistently a distinction between assaults on a basic level and assaults by and by. What this paper shows is that we truly need to begin focusing on the training," composed Matthew Green, cryptography master and educator at Johns Hopkins University. Since the assault is conceivable doesn't mean it is especially simple to do. For Sweet32, the aggressor should have the option to both screen traffic passing between the end client and a weak sites and control JavaScript on a site page stacked by the client's program. It would require around 38 hours to gather many gigabytes of information important to decode the verification treat. This assault situation is a lot of a research center situation, however it's as yet a decent update that in the long run these assaults will become simpler to do.
Endeavors and designers should treat 3DES and Blowfish similarly they treat RC4: quit utilizing it. The intricacy of Sweet32 is tantamount to as of late created assaults against RC4, the scientists said. Analysts growing more approaches to assault RC4 accelerated its expostulation. Significant internet browsers at this point don't uphold RC4, and significant sites, for example, Gmail have additionally completely censured the code. Designers should quit utilizing heritage 64-bit block-figures through and through. On account of Sweet32, that implies debilitating the Triple DES symmetric key code in TLS and resigning Blowfish in OpenVPN. Codes with bigger square sizes, like AES, are safe from Sweet32. Worker overseers can likewise cripple more limited codes completely. This would influence few clients who are as yet depending on more established equipment and programming. There is no compelling reason to stand by till the aggressors are simple and modest to execute to dispose of powerless and weak cryptographic codes. Similarly as there is a purposeful work to jettison RC4, other 64-bit figures additionally need to go
Calculation:
Employments
The employments of 3DES
When the shortcomings of ordinary DES turned out to be more obvious, 3DES was embraced in a wide scope of uses. It was one of the more normally utilized encryption plans before the ascent of AES.
A few instances of its executions included Microsoft Office, Firefox and EMV installment frameworks. A significant number of these stages presently don't utilize 3DES in light of the fact that there are better other options.
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) has delivered a draft proposition saying that all types of 3DES will be censured through 2023 and prohibited from 2024 ahead. In spite of the fact that it's simply a draft, the proposition means the conclusion of a significant time period, and it is clearly beyond an opportunity to move onto other, safer calculations.
Algorithm of TDES:-
The speed of thorough key hunts against DES after 1990 started to cause distress among clients of DES. In any case, clients would not like to supplant DES as it requires some investment and cash to change encryption calculations that are generally taken on and inserted in huge security models. It just so happens, there are two variations of Triple DES known as 3-key Triple DES (3TDES) and 2-key Triple DES (2TDES).
Prior to utilizing 3 TDES, clients initially create and disseminate a 3 TDES key K, which comprises of three unique DES keys K1, K2 and K3. This implies that the real 3 TDES key has length 3×56 = 168 pieces. The encryption plot is shown as
follows −
1) The encryption-decoding measure is as per the following −
2) Encode the plaintext blocks utilizing single DES with key K1.
3) Presently decode the yield of stage 1 utilizing single DES with key K2.
4) At long last, scramble the yield of stage 2 utilizing single DES with key K3.
5) The yield of stage 3 is the ciphertext.
Decoding of a ciphertext is a converse cycle. Clients initially decode utilizing K3, then, at that point scramble with K2, lastly unscramble with K1. Second variation of Triple DES (2TDES) is indistinguishable from 3TDES with the exception of that K3 is supplanted by K1. As such, clients scramble plaintext blocks with key K1, then, at that point unscramble with key K2, lastly encode with K1 once more. In this manner, 2TDES has a vital length of 112 pieces. Triple DES frameworks are altogether safer than single DES, yet these are plainly a much more slow interaction than encryption utilizing single DES.